Estradiol cypionate (EC), is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for trans women, and in hormonal birth control for women. It is given by injection into muscle once every 1 to 4 weeks.
Side effects of estradiol cypionate include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, nausea, headache, and fluid retention. Estradiol cypionate is an estrogen and hence is an agonist of the estrogen receptor, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol.Estradiol cypionate is an estrogen ester and a long-lasting prodrug of estradiol in the body. Because of this, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of estrogen.
Estradiol cypionate was first described as well as introduced for medical use in 1952. Along with estradiol valerate, it is one of the most commonly used esters of estradiol. Estradiol cypionate has mostly been used in the United States, but is also marketed in a few other countries. The medication is not available in Europe.[24] It is not currently available as a generic medication in the United States.
Estradiol
cypionate is a form of estrogen medication used in hormone replacement
therapy (HRT) for transgender women, also known as male-to-female (MTF)
hormone therapy. It is a synthetic form of estradiol, which is the
primary female sex hormone.
Estradiol cypionate is available as
an injectable medication. It is administered via intramuscular
injection, typically into the gluteal (buttock) muscle. The injection is
usually given once every 1 to 2 weeks, depending on the specific dosage
prescribed by a healthcare professional.
The medication works
by mimicking the effects of estrogen in the body. It helps to feminize
the body by promoting breast development, redistributing fat, reducing
muscle mass, softening the skin, and reducing the growth of facial and
body hair.
Injection schedule: Estradiol cypionate is ty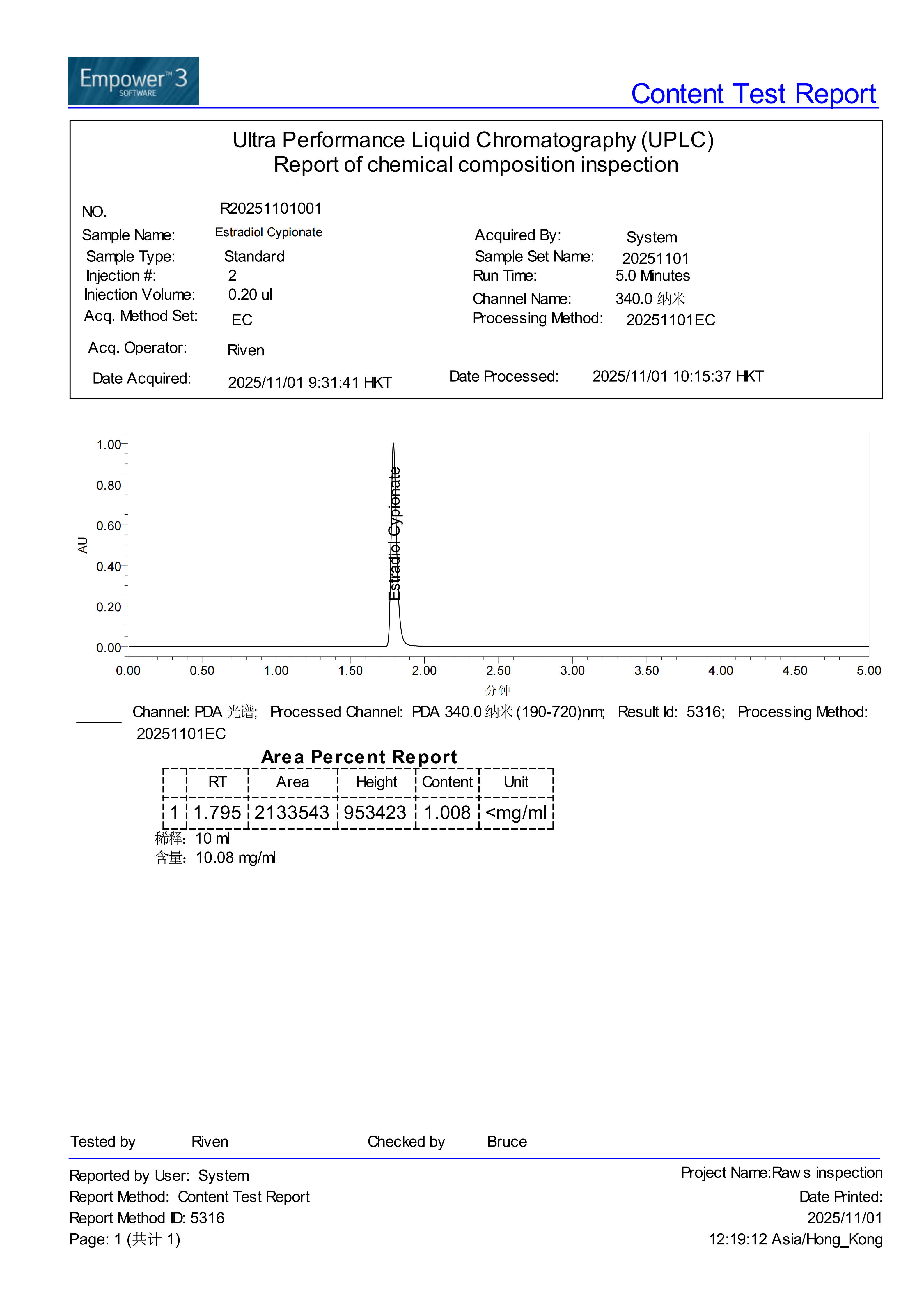 pically given once every 1 to 2 weeks.
pically given once every 1 to 2 weeks.